Introduction
Student Financial Aid Options navigating the world of student financial aid can be overwhelming. With rising tuition costs and the need for advanced degrees, many students find themselves searching for ways to finance their education. Financial aid can be a lifeline, helping to bridge the gap between what families can afford and what students need to pay for their education. Whether you’re a high school senior looking to attend college or a graduate student pursuing further education, understanding the various financial aid options available to you is crucial.
This article will guide you through the different types of student financial aid, how to apply for them, and tips to maximize your financial aid package. We will also explore the benefits and risks associated with different financial aid options to help you make informed funding decisions.
What is Student Financial Aid?
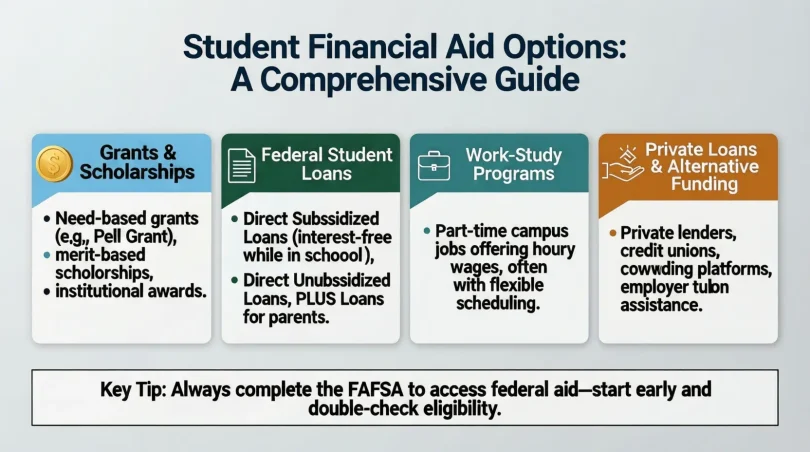
Student financial aid refers to the funding that is available to help students pay for their education. It can come from various sources, including the government, educational institutions, private organizations, and non-profit foundations. Financial aid can help cover tuition, fees, books, and other educational expenses. There are four main types of financial aid: grants, scholarships, loans, and work-study.
- Grants: These are funds given to students that do not need to be repaid, making them highly desirable.
- Scholarships: These are merit-based awards given to students based on their academic, athletic, or other achievements.
- Loans: These are borrowed funds that must be repaid with interest. They are available through federal and private lenders.
- Work-Study: A federal program that allows students to earn money by working part-time during the academic year.
Why is Student Financial Aid Important?

Student financial aid plays a crucial role in making education accessible to a wide range of students, regardless of their financial background. Here are a few reasons why financial aid is so important:
- Reduces Financial Barriers: For many families, paying for college can be a financial burden. Financial aid makes higher education more affordable by helping to cover the cost of tuition and other expenses.
- Increases Access to Education: Financial aid allows students from low-income backgrounds to attend college and pursue their dreams, which may have been otherwise out of reach.
- Improves College Completion Rates: Students who receive financial assistance are more likely to stay in school and complete their degrees. Financial aid can reduce the need for students to work long hours, allowing them to focus on their studies.
- Promotes Economic Mobility: By providing access to education, financial aid helps level the playing field and allows students to improve their earning potential in the future.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide to Student Financial Aid
Step 1: Determine Your Financial Need
Before applying for financial aid, it’s important to assess your financial need. This is typically determined by the difference between the cost of attending school and what you or your family can afford to pay. The government uses a formula known as the Expected Family Contribution (EFC) to calculate this. Many schools and aid programs will use the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) to determine eligibility.
Step 2: Complete the FAFSA
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the first step for most students seeking financial aid. It collects information about your financial situation, including income, family size, and number of family members attending college. The FAFSA is used to determine eligibility for federal grants, loans, and work-study programs. It is also used by many states and schools to award their own financial aid.
- When to Apply: The FAFSA opens each year on October 1st and has deadlines that vary by state and school. Apply early to maximize your chances of receiving financial aid.
- Documents You’ll Need: When filling out the FAFSA, you’ll need documents such as your tax returns, proof of income, and your Social Security number.
Step 3: Explore Other Financial Aid Options
Once you’ve completed the FAFSA, you can begin exploring other financial aid options.
- Scholarships: Many colleges, private organizations, and community foundations offer scholarships. You can apply for these based on your academic performance, extracurricular activities, or field of study.
- Tip: Start by checking with the financial aid office at your school, and search online scholarship databases.
- Grants: There are a variety of federal and state grants available. The most common federal grant is the Pell Grant, which is awarded based on financial need.
- Loans: If you need to borrow money to cover the cost of education, federal loans generally offer the best terms. The two main types of federal loans are Direct Subsidized Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans.
- Work-Study: This program allows you to earn money while attending school, typically through part-time jobs offered on campus.
Step 4: Review Your Financial Aid Package
After submitting your FAFSA and other required documents, you’ll receive a financial aid package from your school. This package will outline the financial aid you’re eligible for, including grants, scholarships, loans, and work-study. Carefully review the package to ensure it covers all your needs.
- Accept or Decline: You’ll need to decide which types of aid you want to accept. You are not obligated to accept loans or work-study, so make sure to weigh the pros and cons.
- Appeal if Necessary: If your financial aid package doesn’t cover your needs, you may be able to appeal for more aid. Contact your school’s financial aid office for guidance.
Benefits of Student Financial Aid
Student financial aid offers numerous benefits, including:
- Affordability: Helps make college more affordable by covering part or all of your tuition and fees.
- Access to Education: Provides opportunities for students who might otherwise be unable to attend college.
- Reduced Financial Stress: Eases the financial burden on students and their families, allowing students to focus on academics.
- Improved Career Opportunities: With access to higher education, students are more likely to secure high-paying jobs in the future.
Disadvantages / Risks of Student Financial Aid
While student financial aid is essential for many students, there are some potential disadvantages to consider:
- Debt from Loans: Loans must be repaid with interest, which can lead to significant debt after graduation.
- Dependence on Aid: Relying heavily on financial aid may make it difficult to budget for life after college, especially if aid is reduced in later years.
- Eligibility Changes: Financial aid eligibility can change, and you may need to reapply each year. Changes in family income or other factors may impact your aid package.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When applying for financial aid, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that could cost you money or delay your aid:
- Missing Deadlines: Ensure you complete the FAFSA and other applications on time to avoid missing out on financial aid.
- Providing Inaccurate Information: Always provide accurate and complete information on your FAFSA to avoid delays or penalties.
- Overlooking Scholarships: Many students overlook scholarship opportunities, missing out on free money. Take the time to search for and apply to scholarships.
FAQs
1. What is the FAFSA, and why is it important?
The FAFSA is a form that determines your eligibility for federal financial aid, including grants, loans, and work-study. It is important because it’s required for most types of financial aid.
2. How do I qualify for a Pell Grant?
Pell Grants are awarded based on financial need, and eligibility is determined through the FAFSA. Generally, students with lower family incomes qualify for Pell Grants.
3. Can I receive financial aid from multiple sources?
Yes, you can receive financial aid from multiple sources, including federal, state, and private organizations. However, the total amount of aid you receive may be limited.
4. What happens if I miss the FAFSA deadline?
If you miss the FAFSA deadline, you may not be eligible for financial aid for that year. Make sure to apply as soon as possible after the FAFSA opens on October 1st.
5. Are student loans the best option?
Student loans can be a good option if you need additional funding, but they should be used cautiously. Federal loans typically offer lower interest rates and better repayment terms than private loans.
6. How do I apply for scholarships?
You can apply for scholarships through your school’s financial aid office, online databases, and private organizations. Be sure to meet all eligibility requirements and submit applications on time.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Start Early: Begin your financial aid search and application process as early as possible to maximize your opportunities.
- Stay Organized: Keep track of all your financial aid documents and deadlines to avoid missing important steps.
- Consider Federal Loans First: Federal loans offer better terms and lower interest rates than private loans, so consider them before seeking other sources of funding.
Conclusion
Funding your education is one of the most important investments you can make for your future. While the cost of education may seem high, there are many smart and practical ways to manage it effectively. Scholarships, grants, part-time work, savings, and student loans all play a role in helping students achieve their academic goals. The key is to understand your options early, plan carefully, and choose funding methods that match your financial situation. With proper planning, education funding becomes a structured process instead of a stressful burden.
Learning how to fund your education also builds strong financial habits that last beyond your student years. Budgeting, saving, and making informed decisions prepare you for real-life financial responsibilities. When you combine discipline with the right funding strategies, you can focus on learning, skill-building, and career growth without constant money worries. In the end, a well-funded education opens doors to better opportunities, confidence, and long-term success.